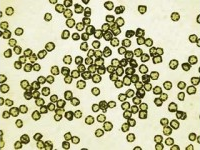
Material Data
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
pH Value | 1.7 × 10⁻⁷/K |
Product Appearance
Product Characterization
Instructions for Use
Nanocellulose is sourced from natural wood fibers and produced using eco-friendly fibrillation technologies, including radiation degradation, mechanochemistry, and ultrasonication.
Applications of Cellulose Nanofibrils
Materials Science: CNFs serve as reinforcing agents, significantly enhancing the strength and toughness of composite materials.
Paper, Textile, and Packaging Industries: Incorporating CNFs improves mechanical properties and barrier performance, leading to more durable and efficient products.
Biomedical Field: Due to their biocompatibility, CNFs are utilized in wound dressings, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
Environmental Sustainability: Derived from renewable resources and biodegradable, CNFs contribute to reducing reliance on petroleum-based products, aligning with eco-friendly initiatives.
Emerging Technologies: Ongoing research indicates promising applications of CNFs in electronics, energy storage, and water treatment, showcasing their potential in innovative fields.
Additional References
Trache, D., et al. (2020). "Nanocellulose: From Fundamentals to Advanced Applications." Frontiers in Chemistry, 8:392. Link
Lin, N., & Dufresne, A. (2014). "Nanocellulose in biomedicine: Current status and future prospect." European Polymer Journal, 59, 302-325. Link
Bhattacharya, M., et al. (2012). "Nanofibrillar cellulose hydrogel promotes three-dimensional liver cell culture." Journal of Controlled Release, 164(3), 291-298. Link
By integrating CNFs, industries can develop products that are not only high-performing but also environmentally sustainable, paving the way for innovative solutions across multiple sectors.